What Are Utility Scale Solar Power Projects?
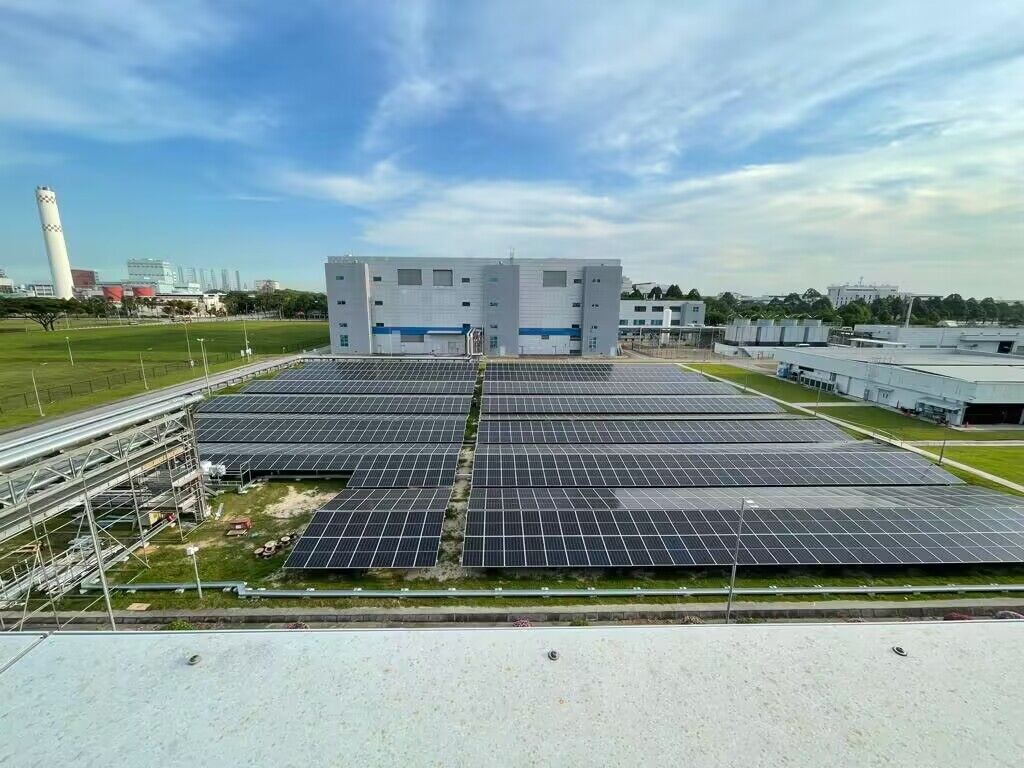
Utility solar design enables projects to generate a large amount of electricity, typically feeding into the utility grid. These utility solar projects are characterized by their significant capacity, often measured in megawatts (MW) or even gigawatts (GW), and require a substantial amount of land to install solar panels.
Increasingly, utility scale solar power plants are paired with battery energy storage systems (BESS) because renewable energy is an intermittent power source. Solar battery banks help utility companies meet peak energy demand with clean energy, which often occurs on summer evenings.
Key features of utility scale solar projects include:
Scale and Solar Capacity: Utility scale solar is designed to generate electricity on a large scale, capable of supplying power to thousands of homes or businesses.
Grid Integration: These utility scale projects are typically connected to the electrical grid, enabling the power generated to be distributed and used by consumers efficiently.
Land Requirements: Utility scale solar power requires a significant amount of land to accommodate the installation of solar panels. The specific land requirements can vary depending on the technology used and the project's capacity, but generally, it ranges from 5 to 10 acres per megawatt of electricity generated.
Lower Cost Solar Electricity: Due to their large size, utility scale solar projects often benefit from economies of scale, making them cost-effective compared to smaller solar installations.
Solar Technology and Components: Utility scale solar power farms utilize various technologies and components, including solar panels, inverters, tracking systems, and transformers, to convert sunlight into electrical energy.
Solar Permitting: These projects often require specific permits, approvals, and compliance with regulations related to land use, environmental impact assessments, and grid interconnection.
GreenLancer specializes in permit-ready solar plan sets, engineering reviews, and interconnection applications. Create an account to begin shopping for utility solar design and engineering services.
Benefits of Utility Scale Solar
Here are the advantages of grid scale solar energy.
Cost-effective solar power: Utility scale solar projects have low operational and maintenance costs, making them financially attractive in the long run.
Job creation and economic growth: These solar projects create employment opportunities, drive innovation, and contribute to strengthening the economy.
Energy storage integration: These solar farms can be paired with battery energy storage systems to provide backup power, manage energy ramps, and enhance grid stability.
Scalability: Utility scale solar power projects can be easily scaled up to meet growing energy demand without significant additional infrastructure.
Sustainability: Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Grid stability and reliability: Utility scale solar power plants can contribute to grid stability, especially when combined with energy storage or other grid management techniques.
Utility Scale Solar Design Challenges
Although utility scale solar is growing significantly, there are project development hurdles to contend with.
Utility Scale Solar Permitting Process
Unfortunately, permitting issues can delay projects or even stop them from progressing. Congested interconnection queues can slow renewable energy project development because interconnection studies can be time-consuming and expensive. Interconnection timelines and costs are among the biggest hurdles to rapid utility scale solar growth. Contact GreenLancer if you need assistance with the utility scale solar permitting process.
Transmission Capacity Expansion
Developers often locate utility scale renewable energy projects far from load centers, so they require transmission capacity expansion to reach electricity markets. Therefore, generation interconnection requests often require transmission network upgrades.
Solar developers often foot part of the bill for needed improvements to the electricity grid, despite many of these upgrades creating system-wide benefits. These costs drive up the cost of solar electricity and create uncertainty as they can be challenging to anticipate.
Considerations for Utility Solar Design
Several crucial factors are carefully considered to ensure the successful planning and operation of projects.
Solar Energy Resource Availability: The first step in utility solar design is to assess the solar resource availability at the project site. This involves analyzing historical weather data, solar insolation levels, and shading patterns to determine the energy potential of the area. Understanding the solar power resource availability is essential for estimating the energy output and therefore the financial viability of the utility scale solar power project.
Land Availability and Site Selection: Identifying suitable land for the solar farm is critical. Factors such as land size, topography, soil conditions, proximity to existing infrastructure, and land ownership rights are considered during the site selection process. Choosing the right location can impact overall project costs, solar energy production, and environmental impacts.
Technology Selection and System Configuration: Selecting the appropriate solar technology and system configuration is essential for optimizing the performance and reliability of the solar farm. Designers must choose between fixed-tilt, single-axis tracking, or dual-axis tracking systems based on site-specific factors like energy production goals, space availability, and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Permitting Requirements: Environmental impact assessments evaluate the potential ecological, social, and visual impacts of the solar project as part of the utility solar design process. Therefore, designers must adhere to regulatory requirements and secure necessary permits for land use, environmental compliance, construction, and operation.
Local Regulations and Stakeholder Engagement: Compliance with local regulations, zoning ordinances, and community engagement are essential aspects of utility solar design. Engaging with stakeholders, addressing community concerns, and obtaining support from local authorities is crucial for successful project development and long-term acceptance.
Utility Scale Solar Projects Are Essential
As concern about greenhouse gas emissions and climate change continues to rise, utility scale PV plants provide a solution. As the installed capacity of solar photovoltaics increases, the demand for fossil fuel power plants decreases. In addition, battery storage systems at solar plants enable solar power to meet peak energy demand, even when the sun isn’t shining.
Utility scale solar comes with its own permit and engineering nuances and challenges – GreenLancer has a network of solar designers and utility scale solar engineers who specialize in AHJs across the country to navigate the process with simplicity.